Batch Denoise Script
This page explains the development of a python script that can batch denoise a sequence of RenderMan .exr image files.
ALGORITHM
1. Use the inspection module to determine the location of the images directory.
2. Create a list of the full paths of the .exr files.
2.1 Sort them.
3. Create a list with numeric extensions.
4. Obtain the name of the first image (excluding numeric and ".exr" extensions).
5. Create the batch denoise file that will allow the user to denoise the images upon running the file.
5.1 Make sure the script will work for both Windows and Linux opperating systems.
5.2 Write the command strings.
5.3 Close the file.
5.4 Print a confirmation that the batch denoise files have been created.
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Place the batch_denoise.py code into the images folder that contain the .exr files that need to be denoised.
2. Execute the script from this location.
3. On Linux double click the file called "run_batch_denoise", on Windows double click the file called "run_batch_denoise.bat".
THE CODE - "batch_denoise.py"
import os
import os.path
import glob
import inspect
import re
# 1. Determine the path and location to the images directory.
fullpath = inspect.getframeinfo(inspect.currentframe()).filename
dirpath = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(fullpath))
projpath = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(dirpath))
# 2. Create a list of the full paths of the .exr files.
glob_patt = os.path.join(dirpath, '*variance.*.exr')
paths = glob.glob(glob_patt)
# 2.1 Sort them.
paths.sort()
# 3. Create a list with numeric extensions.
flist = []
number = re.compile('(\w+)[._](\d+)[._](exr)')
for path in paths:
fname = os.path.basename(path)
fsearch = re.search(number, fname)
fsearch_2 = fsearch.group(2)
flist.append(fsearch_2)
frames = (",".join(flist))
# 4. Obtain the name of the first image (excluding numeric and ".exr" extensions).
frame = os.path.basename(paths[0])
fsearch = re.search(number, frame)
gr1 = fsearch.group(1)
first_frame = ('%s.{%s}.exr'%(gr1,frames))
final_path = os.path.join(dirpath, first_frame)
# 5. Create the batch denoise file that work depending on the OS.
if os.name == 'posix':
# 5.1 Linux
filepath = os.path.join(projpath, 'batch_render_denoise')
f = open(filepath,'w')
# 5.2 Write command string.
f.write('denoise --crossframe -v variance -f default.filter.json '+final_path+'\n')
f.write('read\n')
# 5.3 Close the file.
f.close()
# 5.4 Print a confirmation.
print '"run_batch_denoise" created in project directory'
else:
# 5.1 Windows
filepath = os.path.join(projpath, 'batch_render_denoise.bat')
f = open(filepath, 'w')
# 5.2 Write command string.
f.write('denoise --crossframe -v variance -f default.filter.json '+final_path+'\n')
f.write('pause\n')
# 5.3 Close the file.
f.close()
# 5.4 Print a confirmation.
print '"run_batch_denoise.bat" created in project directory'
PRINTED CONFIRMATION UPON EXECUTION OF THE CODE
The following is placeholder text known as “lorem ipsum,” which is scrambled Latin used by designers to mimic real copy. Fusce at massa nec sapien auctor gravida in in tellus. Sed a ligula quis sapien lacinia egestas. Donec eu est non lacus lacinia semper.
When the "batch_denoise.py" code is executed, there should be a printed confirmation, like in the above image.
DISPLAYED CONTENTS OF THE "run_batch_denoise" FILE
The "run_batch_denoise" file should appear as it does in the above image. All of the .exr files should be listed in a single command line.
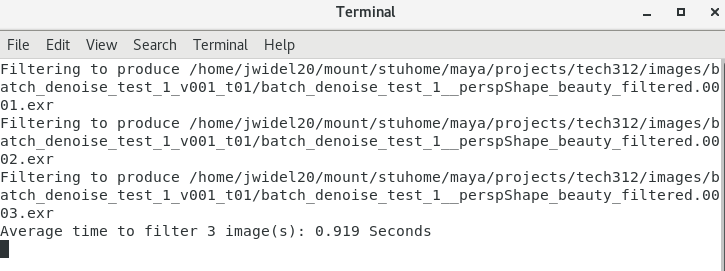
RUNNING THE "run_batch_denoise" SCRIPT
The above image shows the result of running the "run_batch_denoise" file from the terminal.
RESTRICTIONS
This is meant as an example for the process of denoising a batch of rendered .exr files. The code assumes that the script is located in the same directory as the .exr files. This script also assumes that the user needs to denoise .exr files, but another user may wish to denoise .jpg or .png files and must edit the script as a result. This code should be use as a starting point and should be tailored to suit the user's needs.